AERODYNAMIC MODELING
The aerodynamic solution in PARACHUTES is especially designed for gliding parachutes or systems that do not exhibit extensive detached flow in normal operation. Hence, a cost-effective potential flow approach is used to solve the basic aerodynamic field, and semi-empirical models are applied to enhance the solution without increasing the computational cost. The main features of the aerodynamic solver are:
Unsteady panel method with low-order doublets and sources. The wake is developed by a time-marching technique.
Semi-empirical modeling of the wind loads acting on the suspension lines. The cable elements are considered as slender cylinders in traverse flow, and experimental drag coefficients should specified to match the real behaviour of the lines.
Specific aerodynamic force functions can be defined for calculating the wind loads on suspended payloads. These functions can be obtained, for example, by fitting experimental data for a range of body attitudes.
Apparent mass effects due to inertia of the air surrounding the parachute are simulated with the model of Lissaman & Brown.
- The aerodynamic module can be used separately from the structural to solve steady and unsteady aerodynamic configurations.

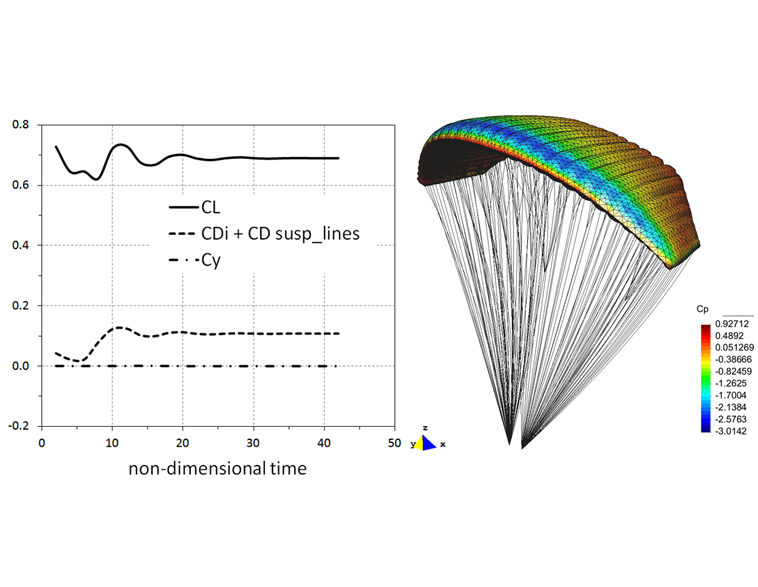
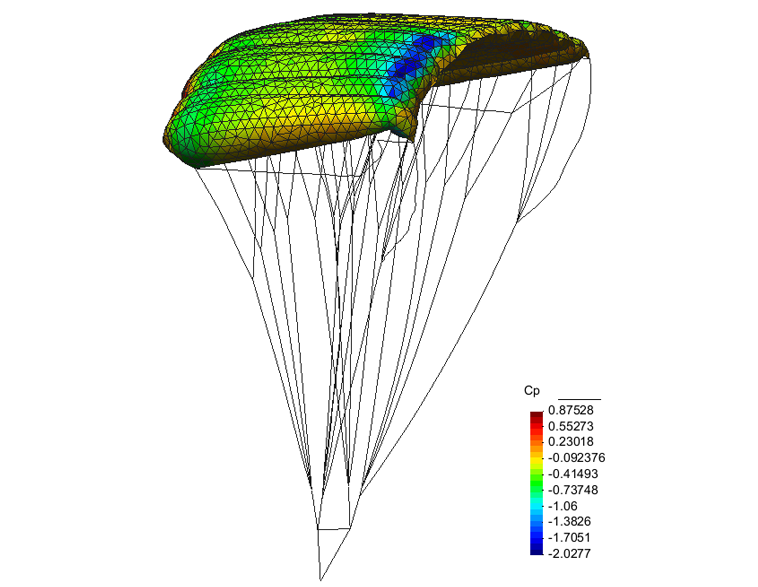
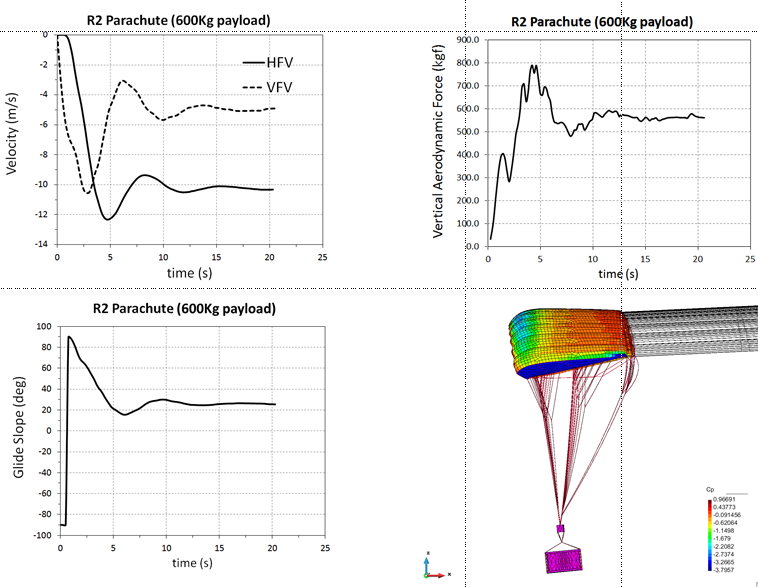
 0
0 1
1 2
2